티스토리 뷰
티켓 판매 애플리케이션 구현하기
여러분은 작은 이벤트를 기획하기로 했다. 이벤트의 내용은 추첨을 통해 선정된 관람객에게 공연을 무료로 관람할 수 있는 초대장을 발송하는 것이다.
한 가지 염두에 둬야 할 점이 있는데, 이벤트에 당첨된 관람객과 그렇지 못한 관람객은 다른 방식으로 입장시켜야 한다는 것이다.
- 이벤트에 당첨된 관람객은 초대장을 티켓으로 교환한 후에 입장할 수 있다.
- 이벤트에 당첨되지 않은 관람객은 티켓을 구매해야만 입장할 수 있다.
코드
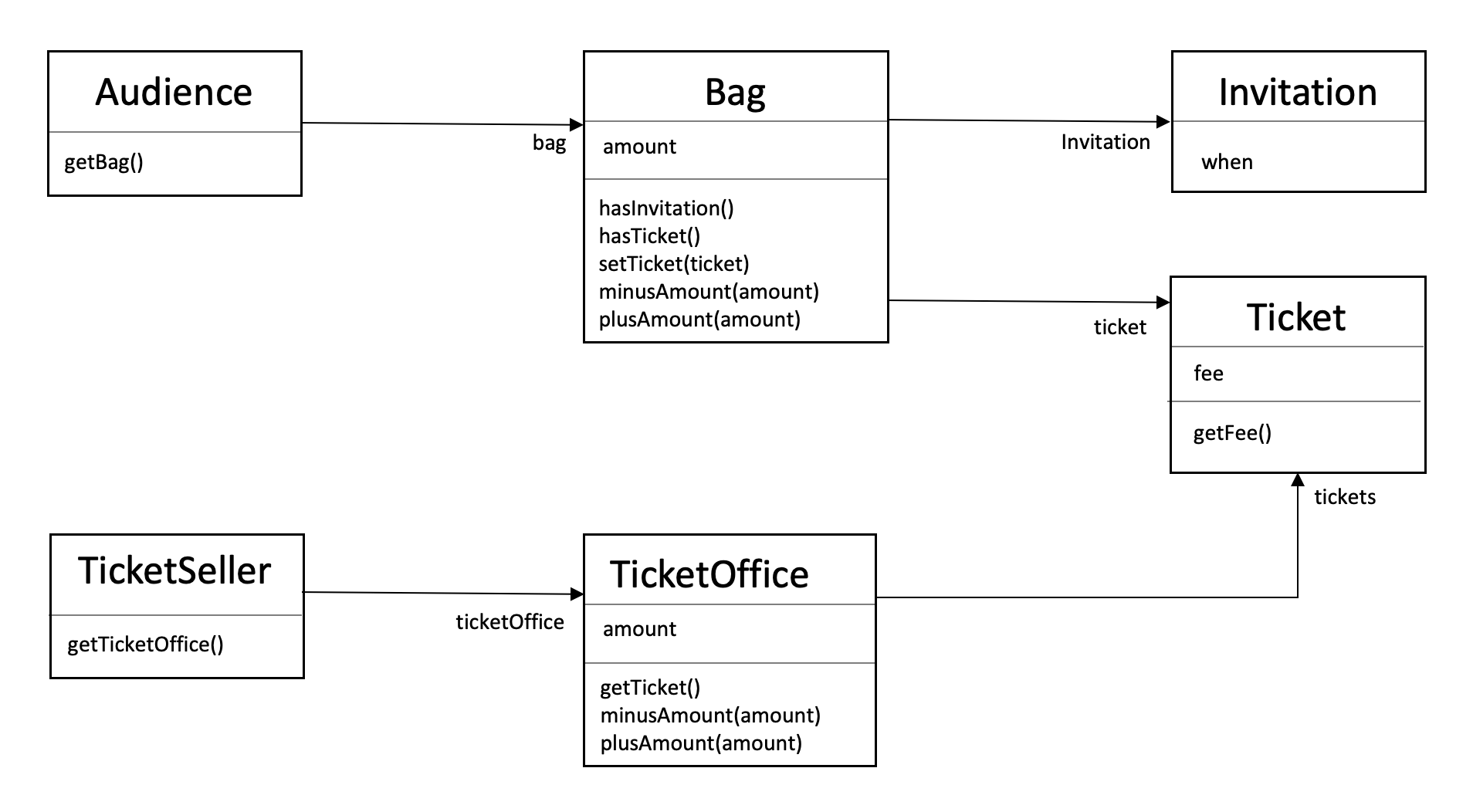
Invitation
공연을 관람할 수 있는 초대일자 (when) 를 인스턴스 변수로 포함하는 간단한 클래스다.
public class Invitation {
private LocalDateTime when;
}
Ticket
공연을 관람하기 원하는 모든 사람들은 티켓을 소지하고 있어야만 한다.
public class Ticket {
private Long fee;
public Long getFee() {
return fee;
}
}이벤트 당첨자는 티켓으로 교환할 초대장을 가지고 있을 것이다. 이벤트에 당첨되지 않은 관람객은 티켓을 구매할 수 있는 현금을 보유하고 있을 것이다.
따라서 관람객이 가지고 올 수 있는 소지품은 초대장, 현금, 티켓 세 가지 뿐이다.
Bag
관람객은 소지품을 보관할 용도로 가방을 들고 올 수 있다고 가정하자.
- 초대장 (Invitation), 티켓 (Ticket), 현금 (Amount) 인스턴스 변수
- 초대장의 보유 여부를 판단하는 hasInvitation 메서드
- 티켓의 소유 여부를 판단하는 hasTicket 메서드
- 현금을 증가시키거나 감소시키는 plusAmount와 minusAmount 메서드
- 초대장을 티켓으로 교환하는 setTicket 메서드
public class Bag {
private Long amount;
private Invitation invitation;
private Ticket ticket;
public boolean hasInvitation() {
return invitation != null;
}
public boolean hasTicket() {
return ticket != null;
}
public void setTicket(Ticket ticket) {
this.ticket = ticket;
}
public void minusAmount(Long amount) {
this.amount -= amount;
}
public void plusAmount(Long amount) {
this.amount += amount;
}
}
이벤트에 당첨된 관람객의 가방 안에는 현금과 초대장이 들어있지만 이벤트에 당첨되지 않은 관람객의 가방 안에는 초대장이 들어있지 않을 것이다.
따라서 Bag 인스턴스의 상태는 현금과 초대장을 함께 보관하거나, 초대장 없이 현금만 보관하는 두 가지 중 하나일 것이다.
Bag의 인스턴스를 생성하는 시점에 이 제약을 강제할 수 있도록 생성자를 추가하자.
public class Bag {
public Bag(long amount) {
this(null, amount);
}
public Bag(Invitation invitation, long amount) {
this.invitation = invitation;
this.amount = amount;
}
}
Audience
관람객은 소지품을 보관하기 위해 가방을 소지할 수 있다.
public class Audience {
private Bag bag;
public Audience(Bag bag) {
this.bag = bag;
}
public Bag getBag() {
return bag;
}
}
TicketOffice
TicketOffice는 판매하거나 교환해 줄 티켓의 목록 (tickets) 과 판매 금액 (amount) 을 인스턴스 변수로 포함한다.
public class TicketOffice {
private Long amount;
private List<Ticket> tickets = new ArrayList<>();
public TicketOffice(Long amount, Ticket ... tickets) {
this.amount = amount;
this.tickets.addAll(Arrays.asList(tickets));
}
public Ticket getTicket() {
return tickets.remove(0);
}
public void minusAmount(Long amount) {
this.amount -= amount;
}
public void plusAmount(Long amount) {
this.amount += amount;
}
}
TicketSeller
판매원은 매표소에서 초대장을 티켓으로 교환해 주거나 티켓을 판매하는 역할을 수행한다.
판매원을 구현한 TicketSeller 클래스는 자신이 일하는 매표소 (ticketOffice) 를 알고 있어야 한다.
public class TicketSeller {
private TicketOffice ticketOffice;
public TicketSeller(TicketOffice ticketOffice) {
this.ticketOffice = ticketOffice;
}
public TicketOffice getTicketOffice() {
return ticketOffice;
}
}
Theater
Theater 클래스가 관람객을 맞이할 수 있도록 enter 메서드를 구현하자.
public class Theater {
private TicketSeller ticketSeller;
public Theater(TicketSeller ticketSeller) {
this.ticketSeller = ticketSeller;
}
public void enter(Audience audience) {
if (audience.getBag().hasInvitation()) {
Ticket ticket = ticketSeller.getTicketOffice().getTicket();
audience.getBag().setTicket(ticket);
} else {
Ticket ticket = ticketSeller.getTicketOffice().getTicket();
audience.getBag().minusAmount(ticket.getFee());
ticketSeller.getTicketOffice().plusAmount(ticket.getFee());
audience.getBag().setTicket(ticket);
}
}
}
안타깝게도 이 작은 프로그램은 몇 가지 문제점을 가지고 있다.
'책 > 오브젝트' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 오브젝트 1-4. 객체지향 설계 (0) | 2023.01.04 |
|---|---|
| 오브젝트 1-3. 설계 개선하기 (0) | 2022.12.22 |
| 오브젝트 1-2. 무엇이 문제인가 (0) | 2022.11.20 |
| 오브젝트 0-2. 프로그래밍 패러다임 (0) | 2022.11.18 |
| 오브젝트 0-1. 패러다임의 시대 (0) | 2022.11.17 |
